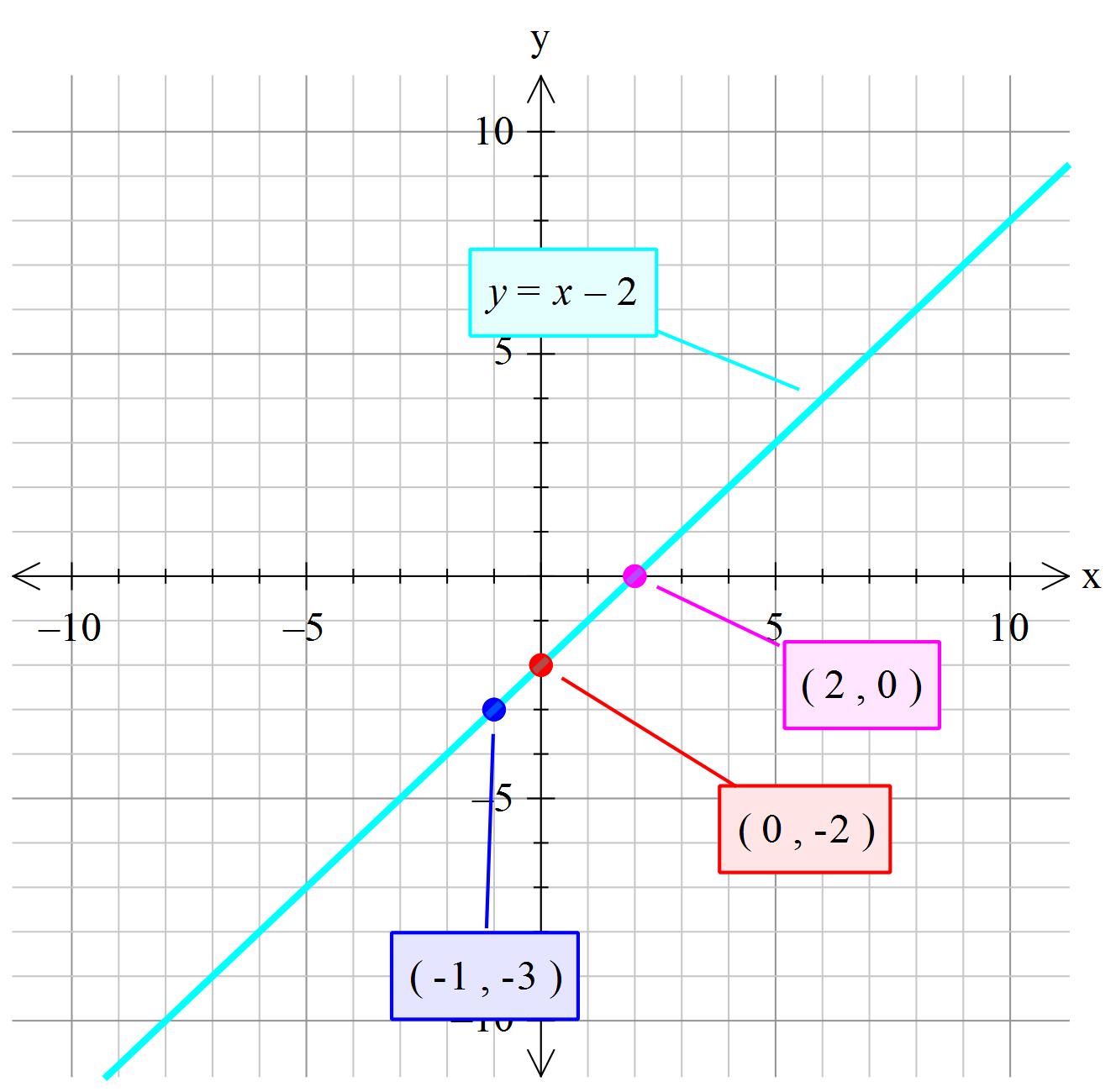
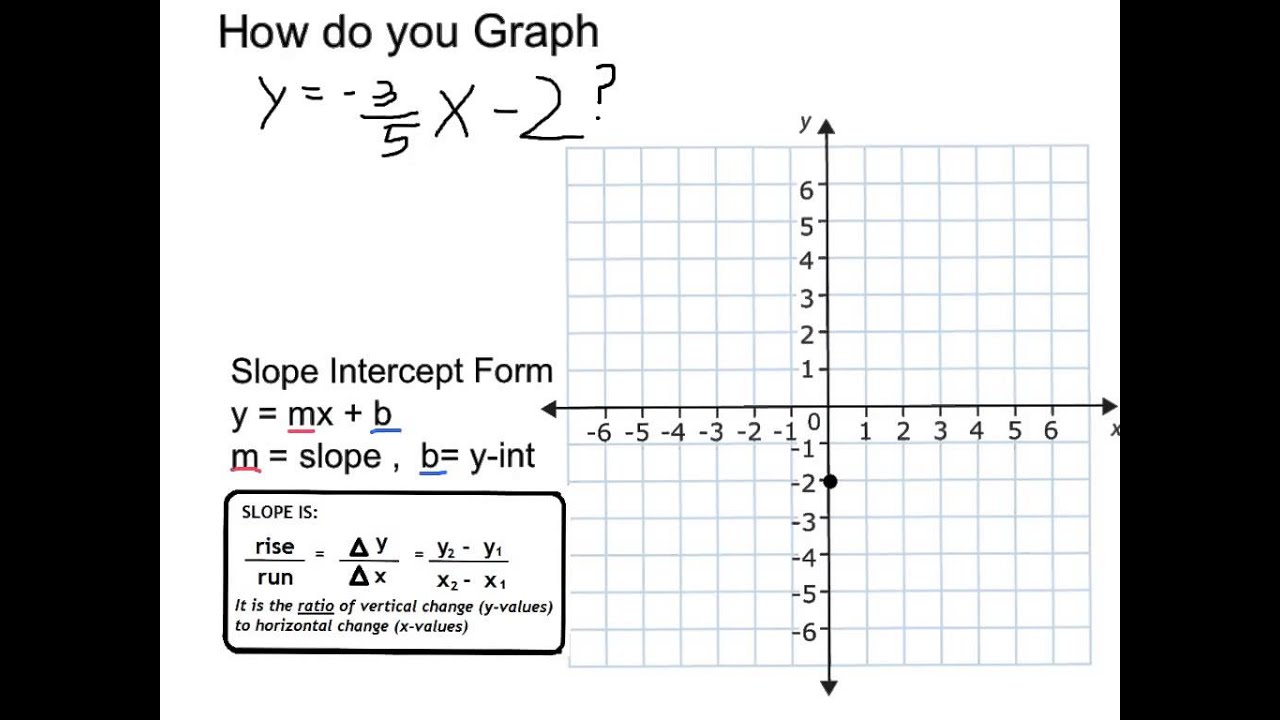
A x B y = C, where A and B are not both zero, is called a linear equation in two variables Here is an example of a linear equation in two variables, x and y The equation y = −3 x 5 y = −3 x 5 is also a linear equation But it does not appear to be in the form A x B y = C A x B y = C
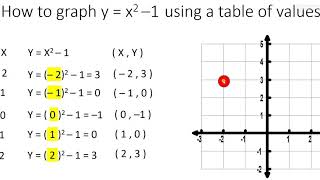
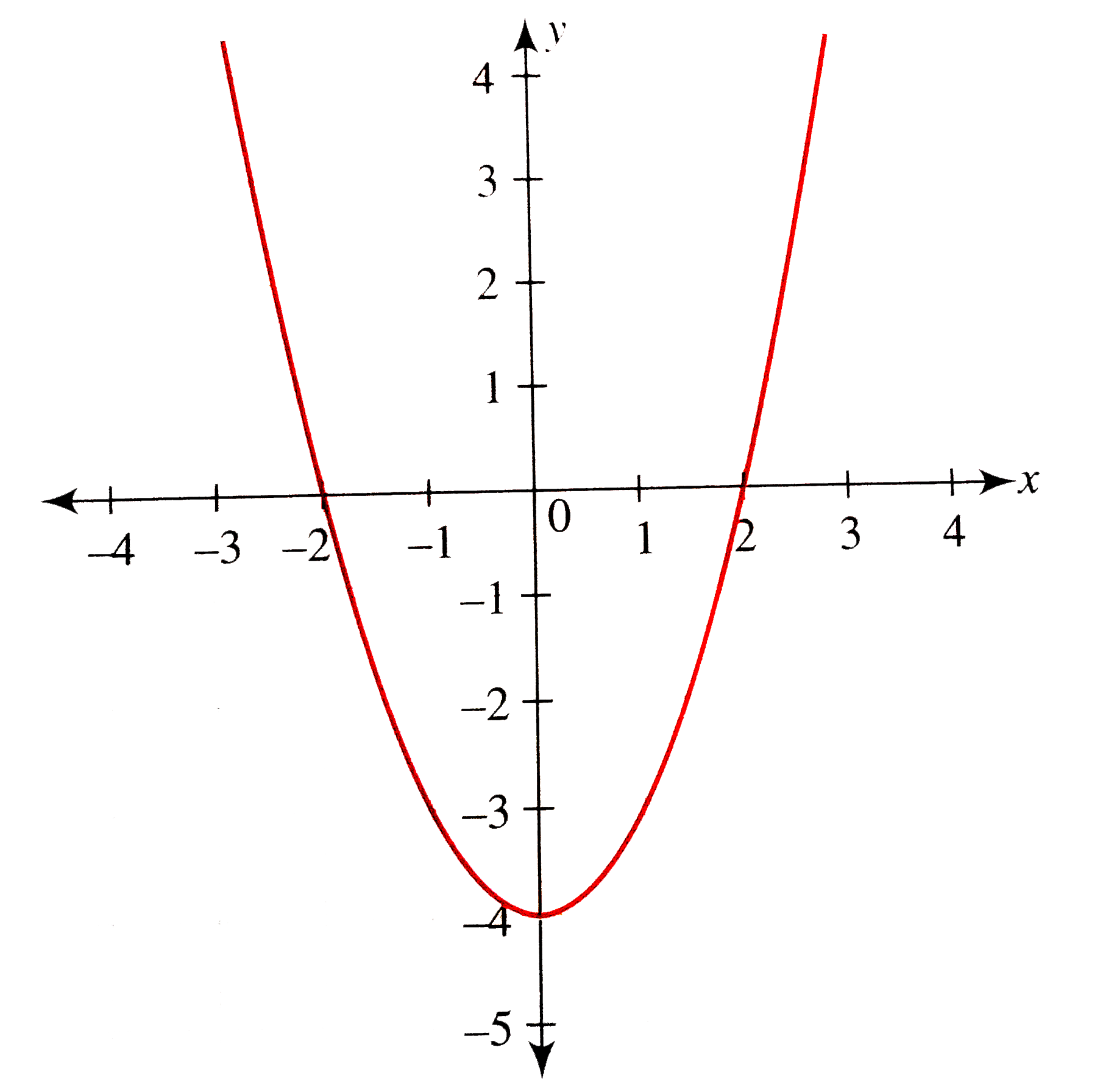
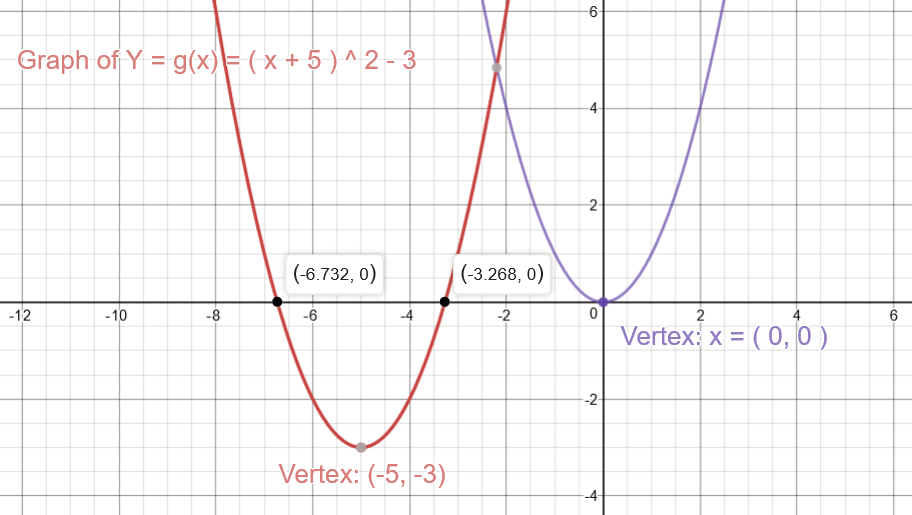
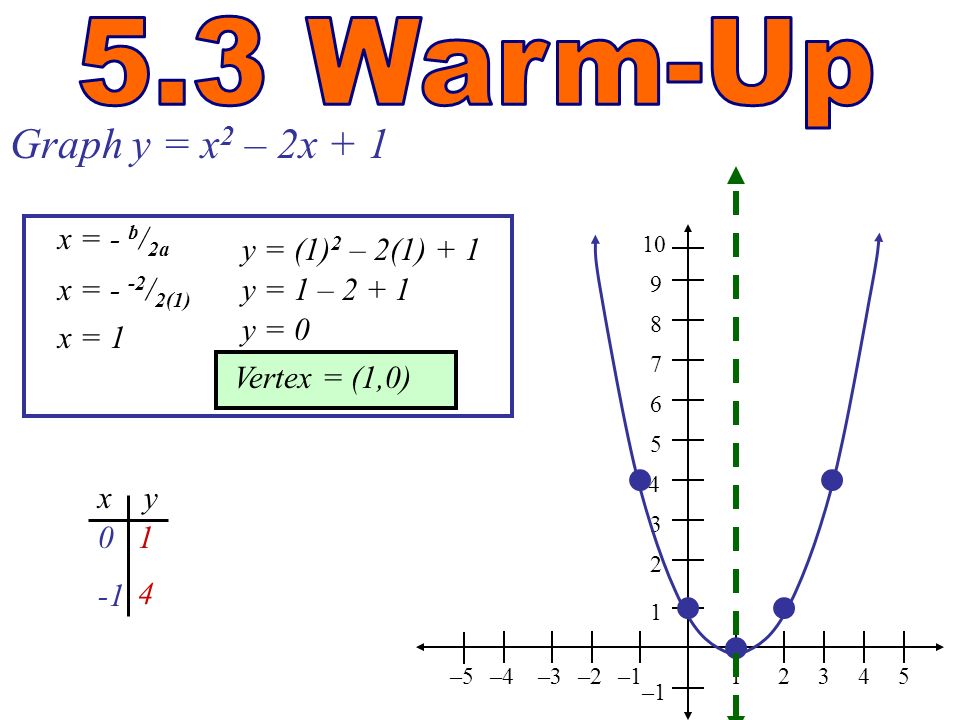
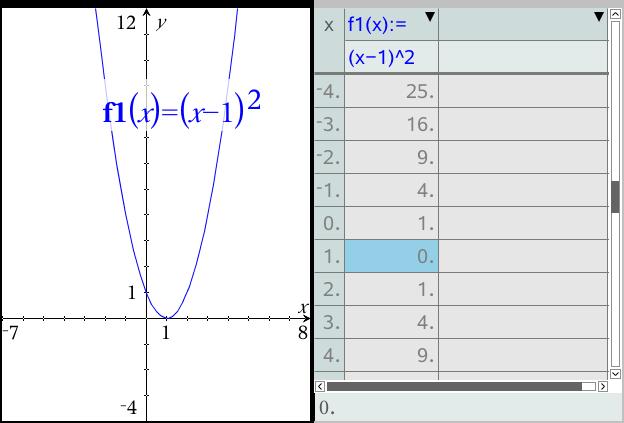
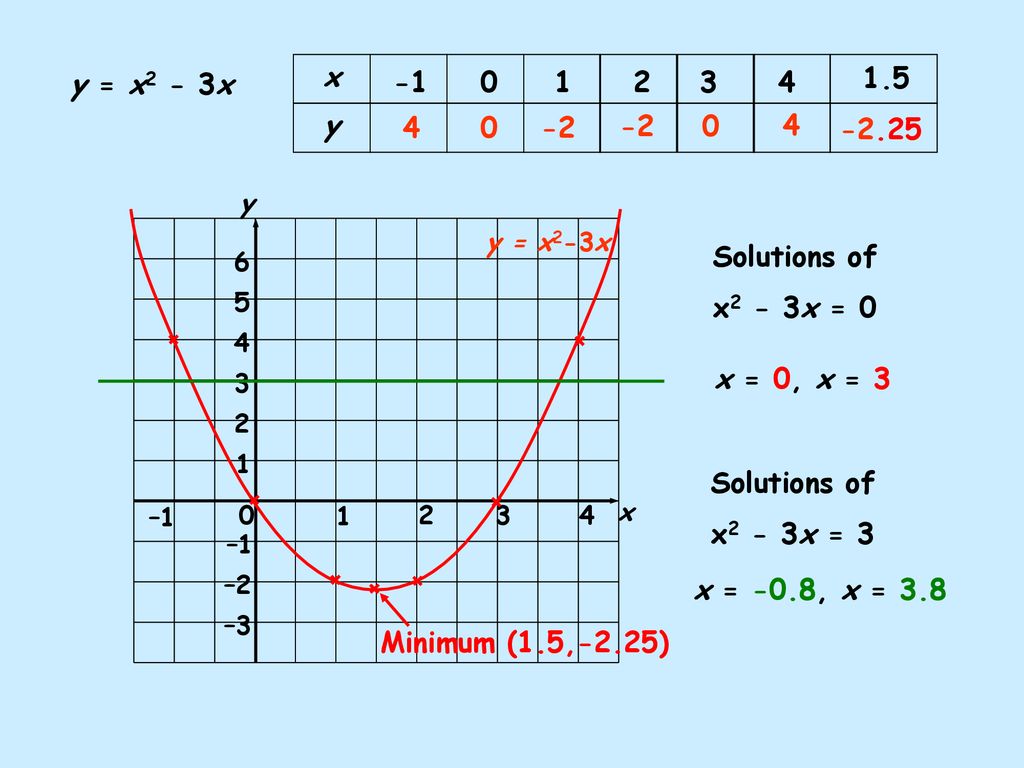
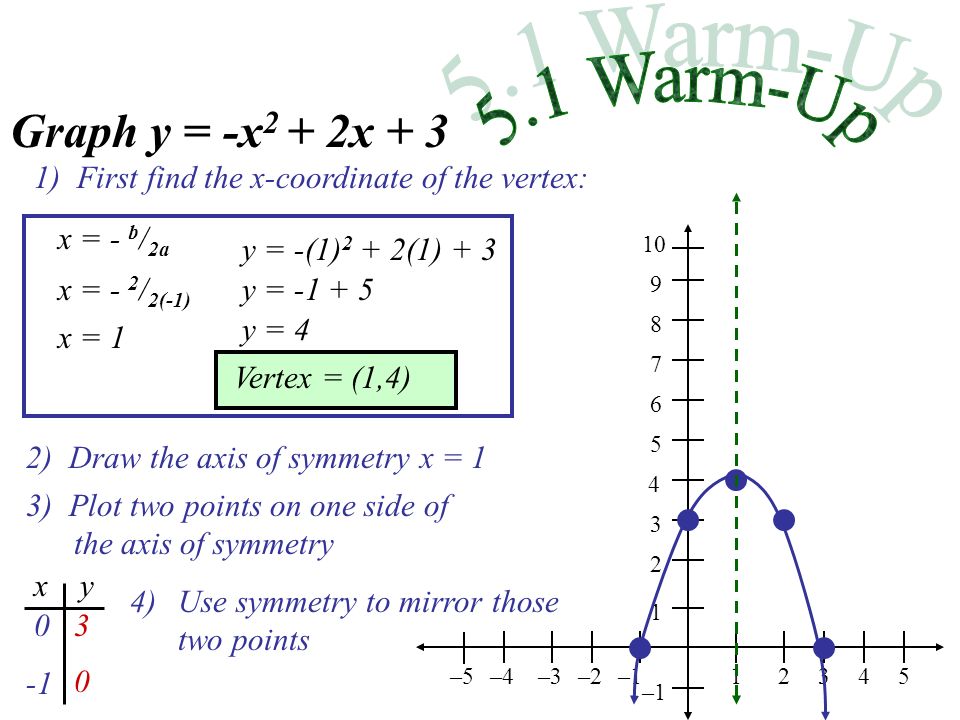
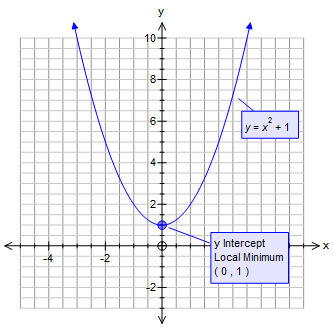
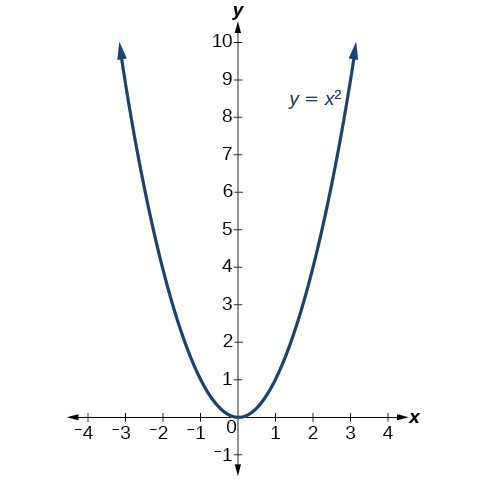
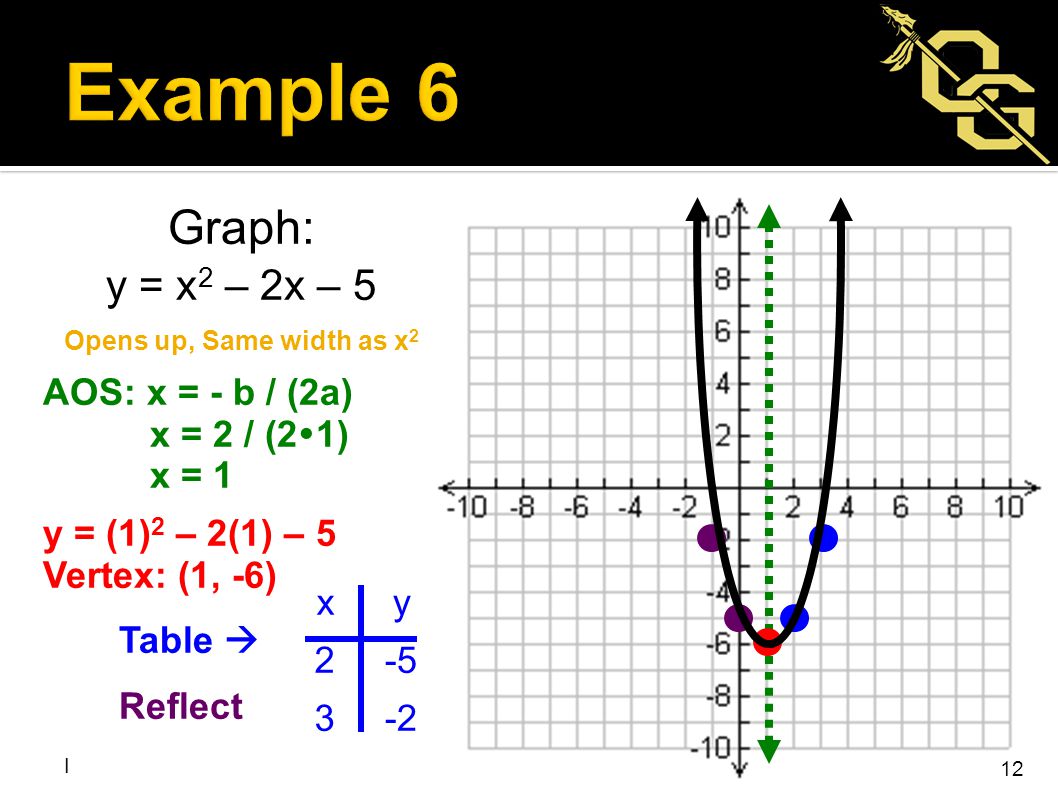
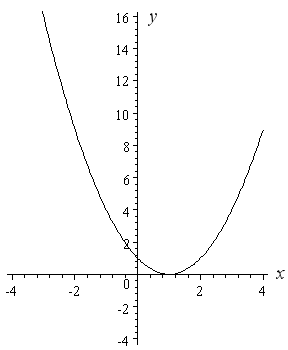
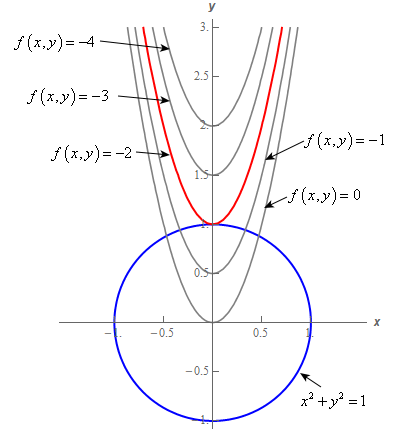
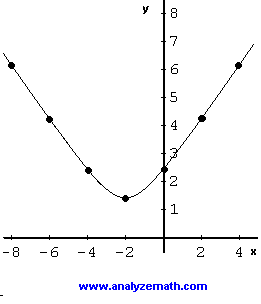
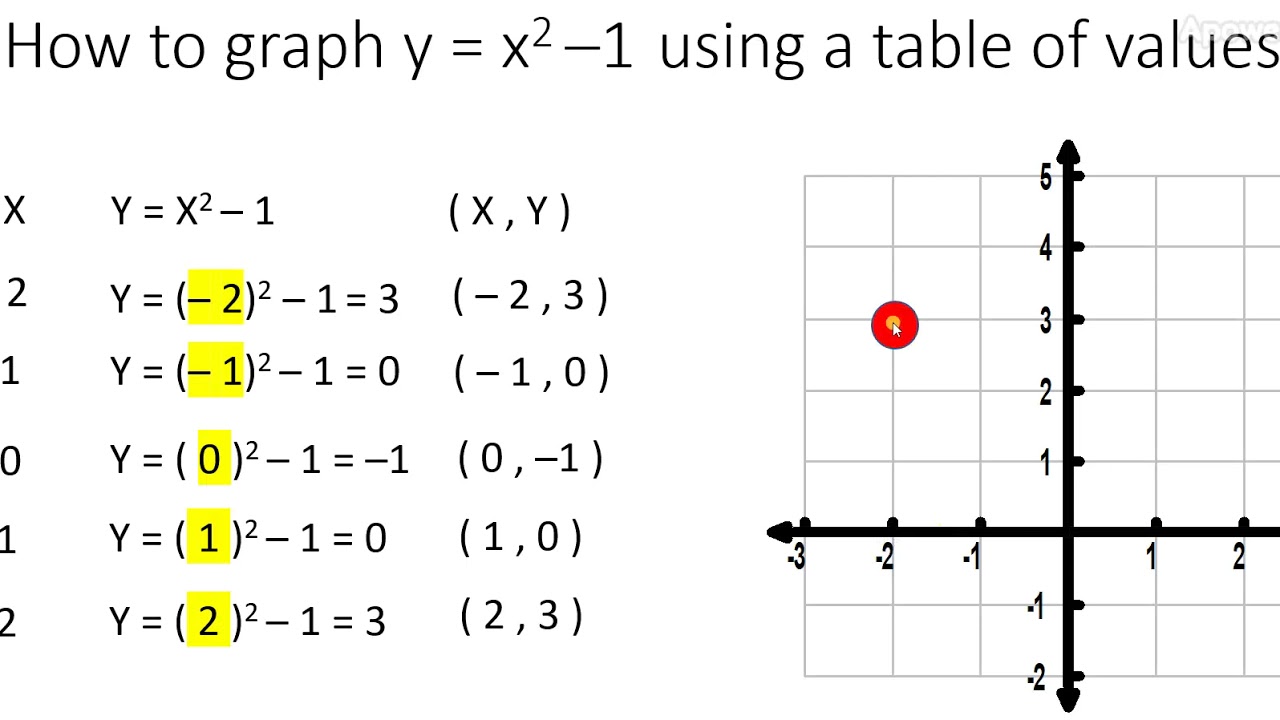
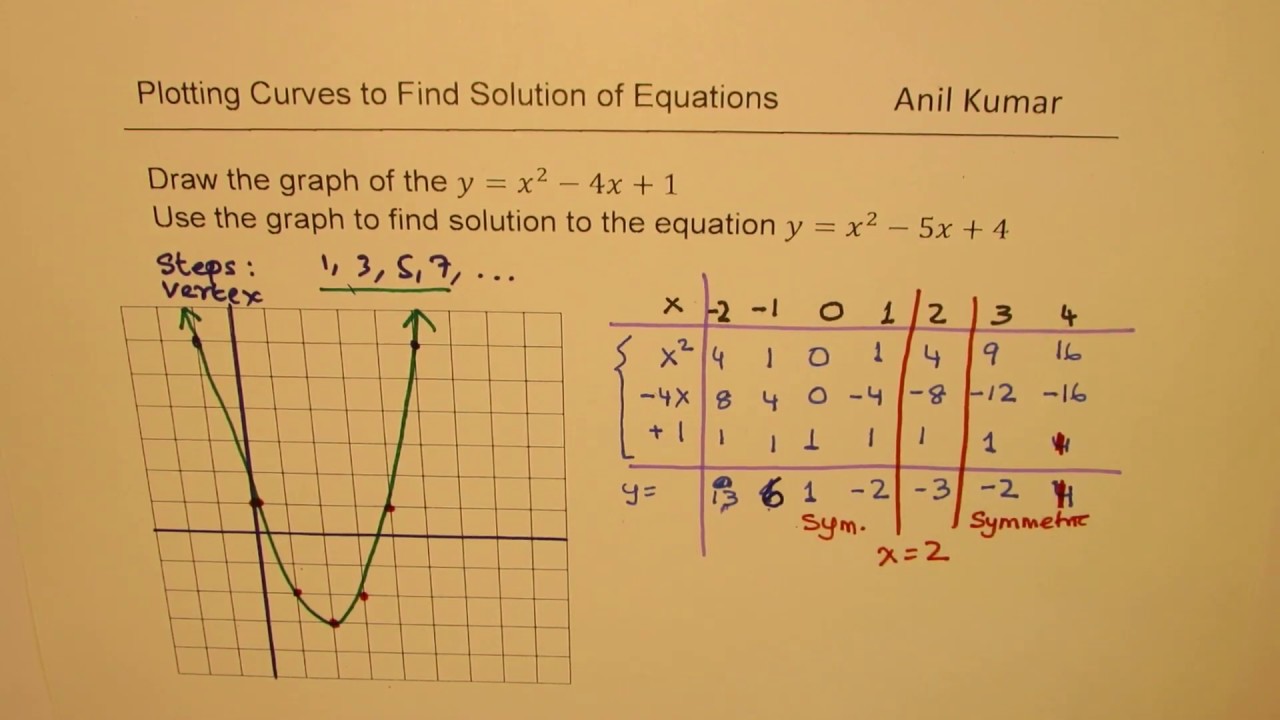
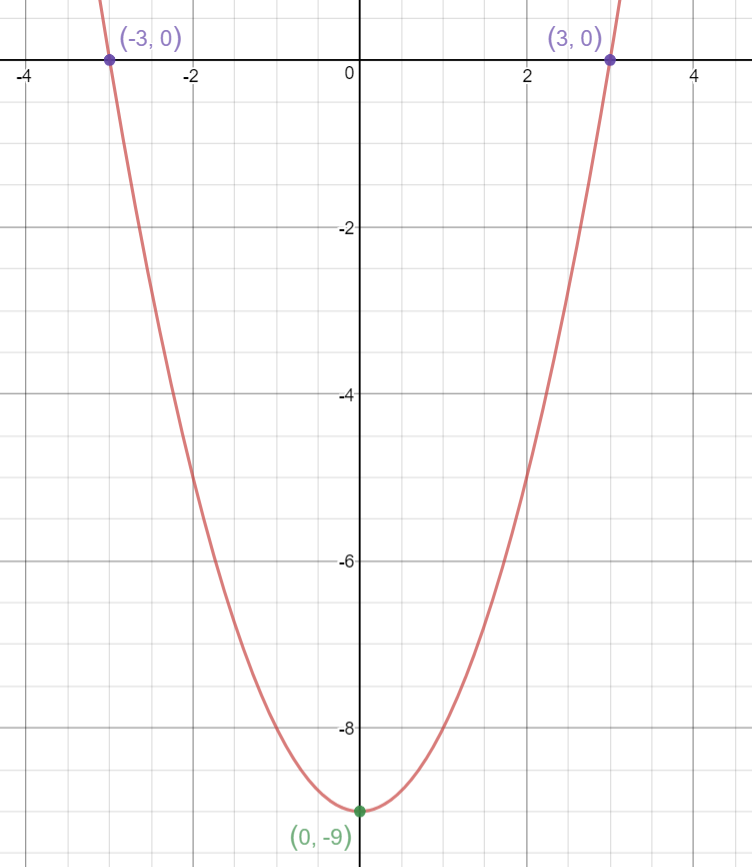
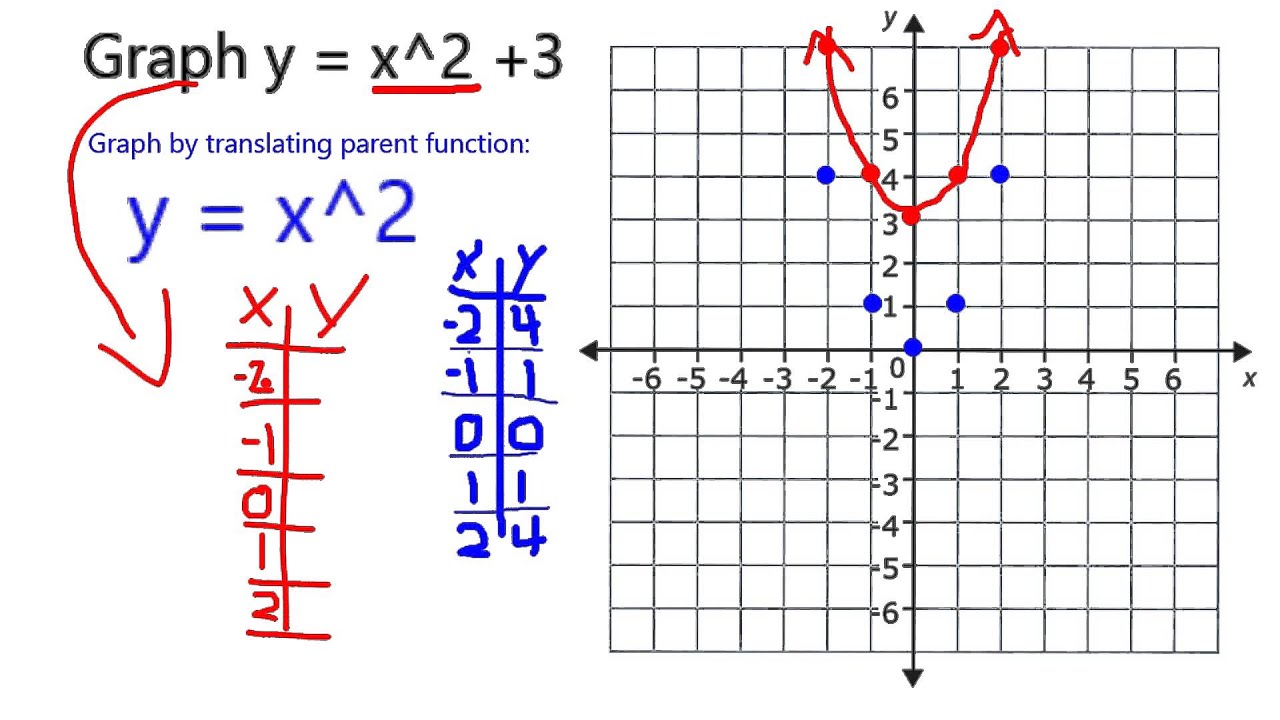
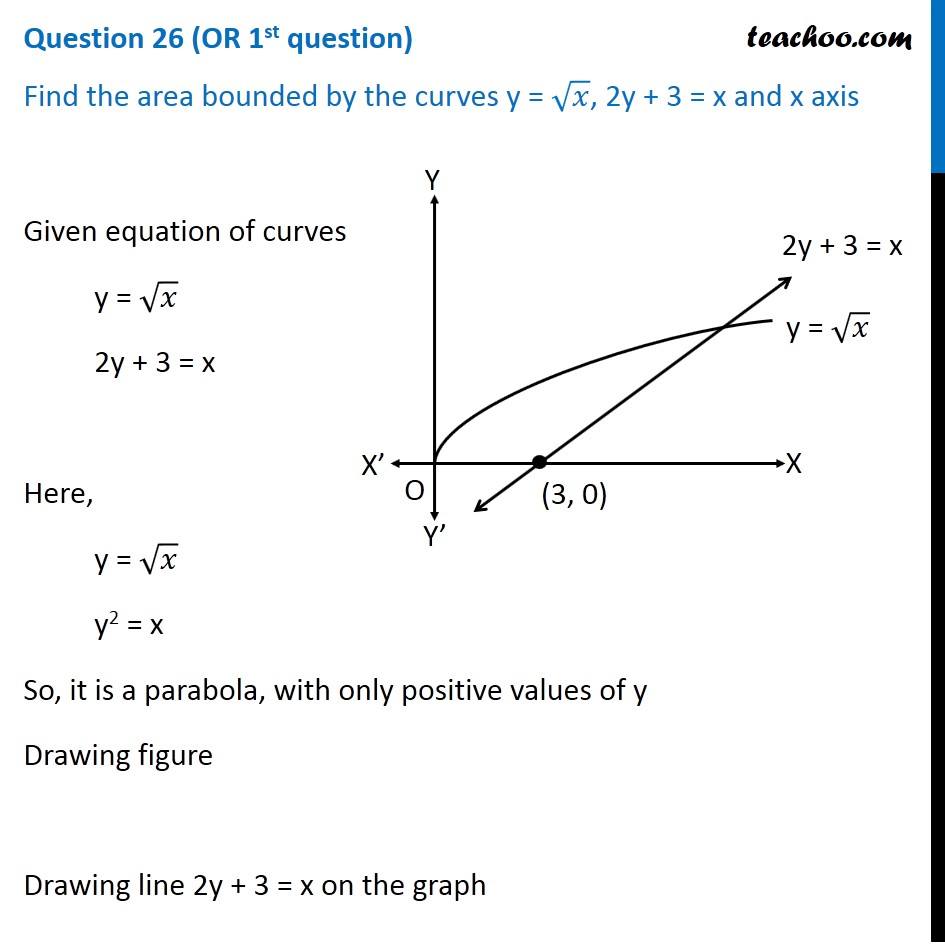
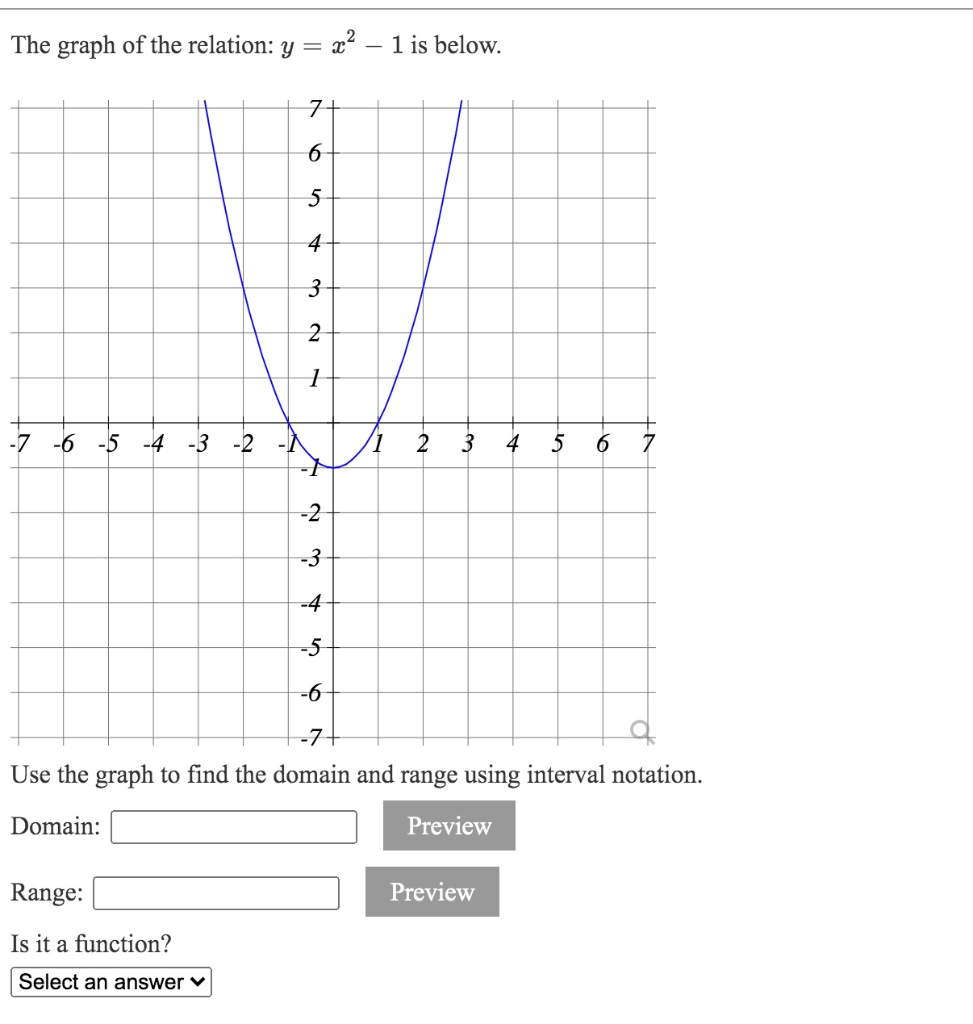
X^2 (y-x^(2/3))^2=1 graph-Plot x^2y^2x Natural Language;Graph the parabola, y =x^21 by finding the turning point and using a table to find values for x and y
X^2 (y-x^(2/3))^2=1 graphのギャラリー
各画像をクリックすると、ダウンロードまたは拡大表示できます
 |  |  |
 |  |  |
 |  | |
 | ||
「X^2 (y-x^(2/3))^2=1 graph」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 |  | |
 | ||
 |  | |
 | ||
「X^2 (y-x^(2/3))^2=1 graph」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 | 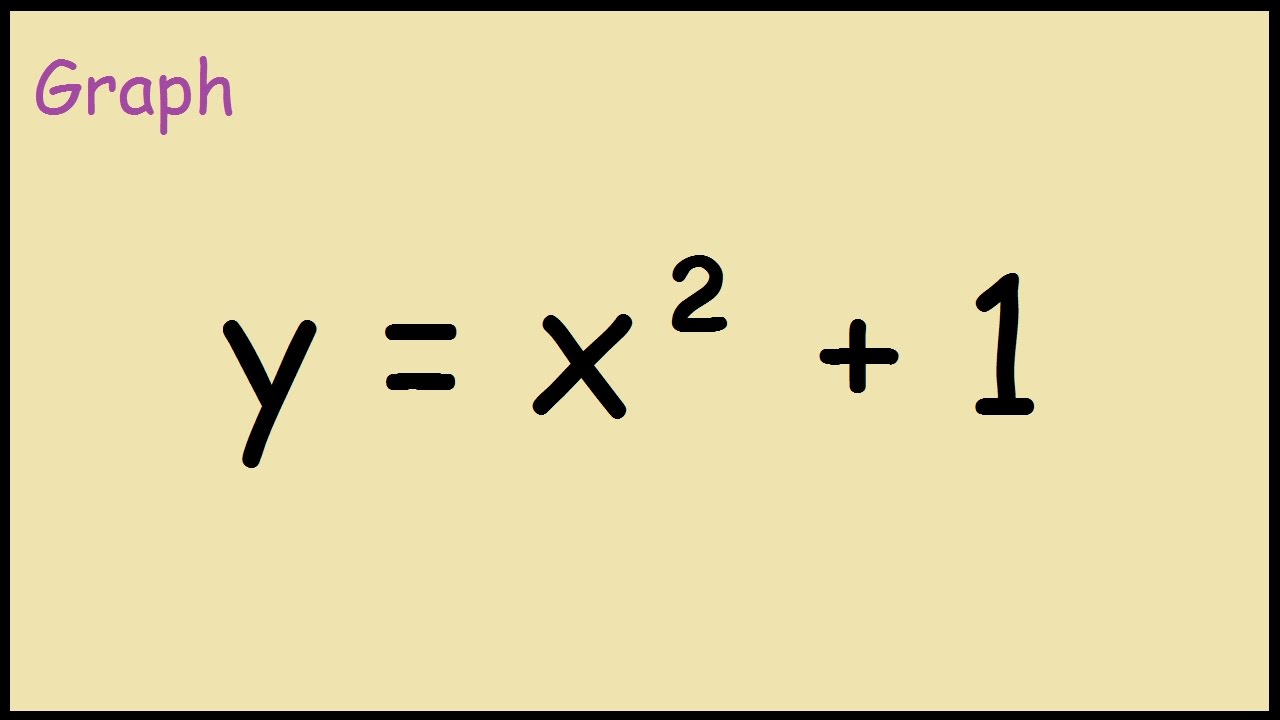 | |
 |  |  |
 |  |  |
 | ||
「X^2 (y-x^(2/3))^2=1 graph」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 |  | |
 |  |  |
 | 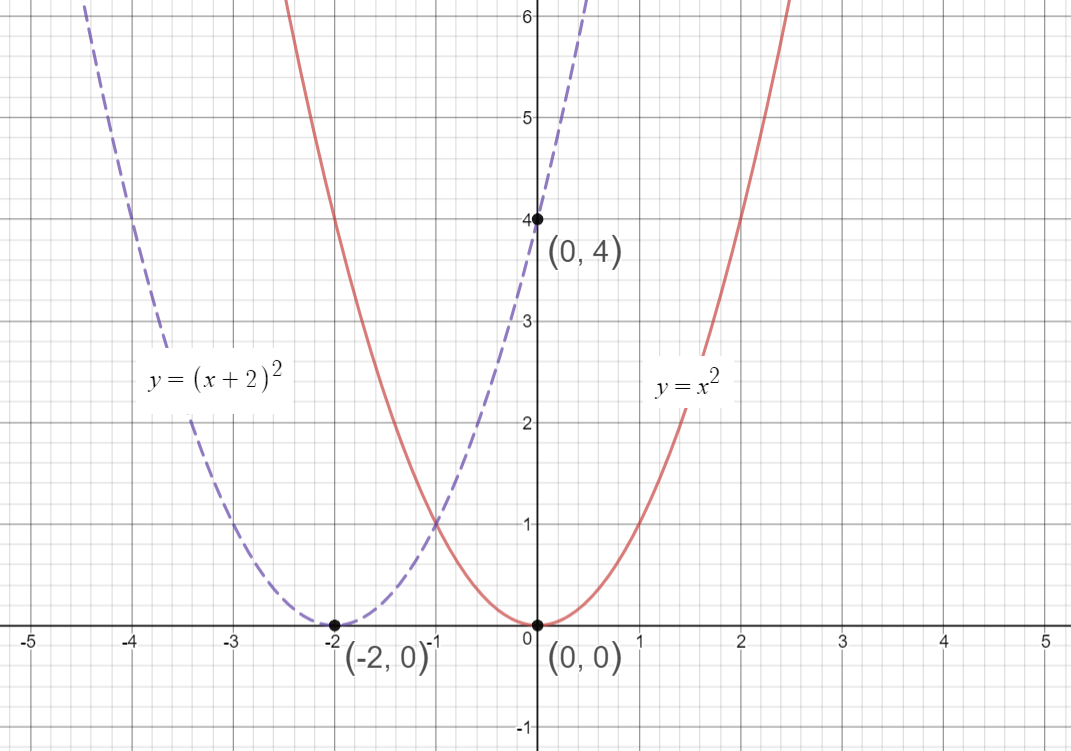 |  |
 |  | |
「X^2 (y-x^(2/3))^2=1 graph」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
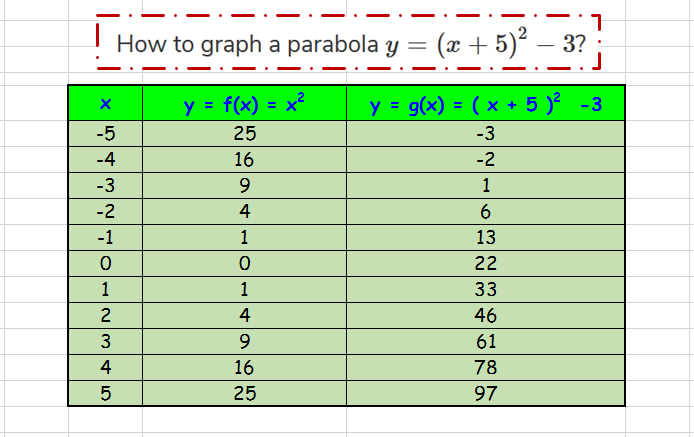
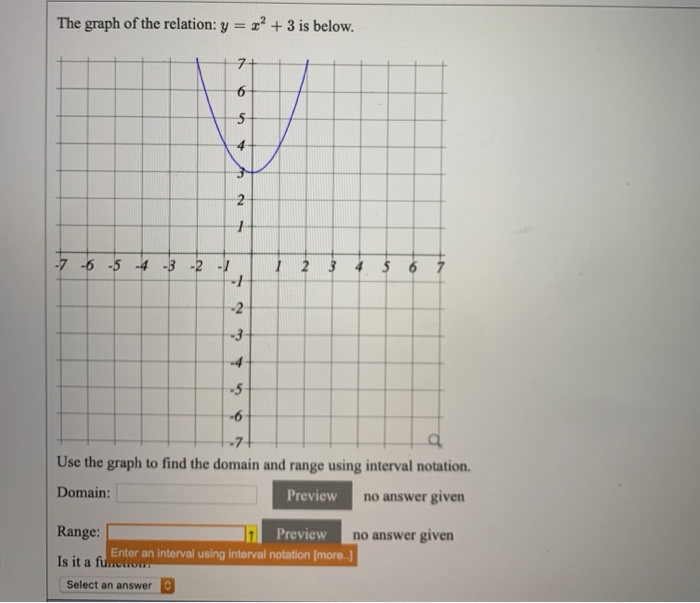 | ||
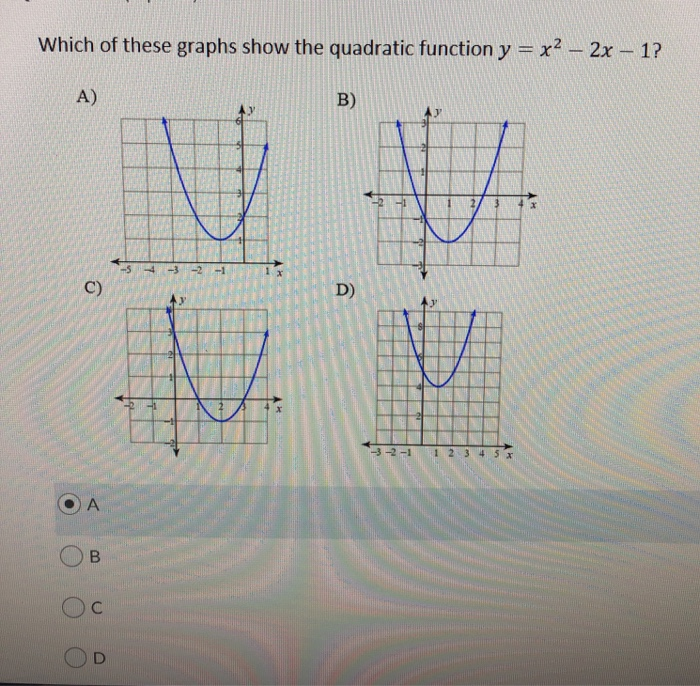 | ||
 |  |  |
 | ||
「X^2 (y-x^(2/3))^2=1 graph」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 |  | |
 | ||
 |  |  |
 |  | |
「X^2 (y-x^(2/3))^2=1 graph」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 |  | |
 |  | |
 |  |  |
 |  |  |
「X^2 (y-x^(2/3))^2=1 graph」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 |  |  |
 |  | |
 |  |  |
 |  | |
「X^2 (y-x^(2/3))^2=1 graph」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 |  | |
 | ||
 |  |
Choose one of the equations and solve it for x by isolating x on the left hand side of the equal sign 3x2y=22 3 x 2 y = 2 2 Subtract 2y from both sides of the equation Subtract 2 y from both sides of the equation 3x=2y22 3 x = − 2 y 2 2 Divide both sides by 3 Divide both sides by 3Divide 1, the coefficient of the x term, by 2 to get \frac{1}{2} Then add the square of \frac{1}{2} to both sides of the equation This step makes the left hand side of the equation a perfect square





0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿